
香港理工大學的Wai Sze YIP、Suet TO研究團隊在《Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering》2024年8月刊發表了題為“3D printing for ultra-precision machining: current status, opportunities, and future perspectives”的綜述型論文,文章概述了用于3D打印的超精密加工(UPM)技術的現狀,分析了將UPM與3D打印相結合的好處,并進一步討論了將這兩種先進制造技術融入潛在行業的未來前景。
研究背景
UPM和3D打印是兩項極具潛力的新興技術,UPM遵循減材制造原理,3D打印基于快速成型和增材制造原理。然而,3D打印技術雖然有一定的優勢,但在精度、表面質量等方面仍存在不足,因此提出將3D打印和UPM技術相結合。本文描述了UPM和3D打印技術的突出特點和來源。詳細闡述了兩種技術結合的優勢和應用,并對這種技術結合的前瞻性發展進行了評估。研究的目的是利用先進制造和加工技術的能力來推動行業進步并彌合相關研究領域的現有差距。
主要研究內容
UPM基于減材制造原理,通過銑削、研磨和拋光等方法實現納米級加工精度,廣泛應用于激光、光學、電子等領域,但存在材料去除率低和可持續性問題。其使用的刀具如金剛石刀具,對加工質量至關重要,且表面生成機制受多種因素影響,模擬建模和人工智能技術可輔助優化加工過程。
3D打印基于增材制造原理,能制造復雜結構零件,具有材料浪費少、成本效益高等優點,但存在精度、表面質量和材料等方面的挑戰。該技術分為擠出式和基于激光的增材制造等類型,在航空航天、生物醫學等領域有廣泛應用,也可用于傳統加工,如制造模具、復雜結構件等。
3D打印在工業應用中存在局限性,如打印材料缺陷、表面質量差、尺寸精度受多種因素影響等,在微尺度制造商業化方面也面臨挑戰。不同的3D打印技術各有優缺點,如選擇性激光燒結(SLS)設備和材料成本高,熔融沉積建模(FDM)有明顯打印痕跡等。
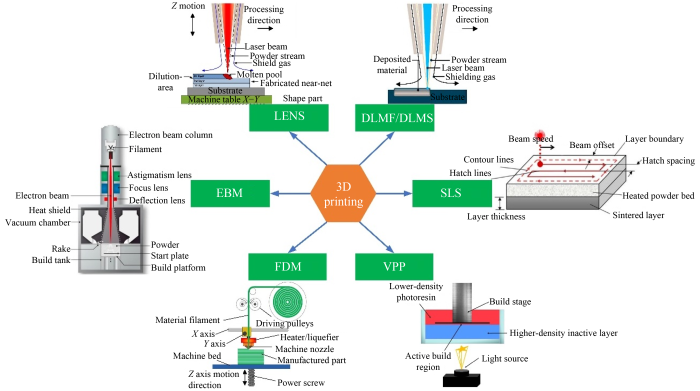
圖 1 當前主流的3D打印技術
3D打印技術可制造多種材料的切削刀具,如硬質合金、陶瓷和金剛石刀具等,具有獨特結構和性能優勢,能提高加工性能,在UPM中有市場潛力。對3D打印部件進行UPM可解決其表面質量、尺寸精度和機械性能等問題,在模具、光學、機械和微電子等領域有重要應用,能提升產品質量和性能。UPM后處理可改善3D打印部件的表面光潔度、尺寸精度和材料性能,在生物醫學領域,兩者結合對實現臨床應用潛力至關重要。
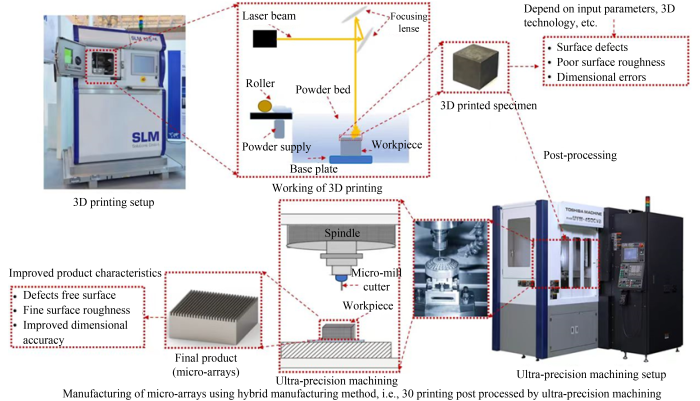
圖2 提出的用于微結構制造的UPM和3D結合打印
UPM與3D打印技術的結合在工具、模具和生物醫學等行業有廣闊前景,可提高工具性能和定制性、改善模具功能和表面完整性、推動醫療設備研發。未來研究應聚焦于提高智能3D打印和智能UPM技術水平和有效性,實現兩者更深度融合,以拓展應用領域,促進工業生產和加工效率提升。
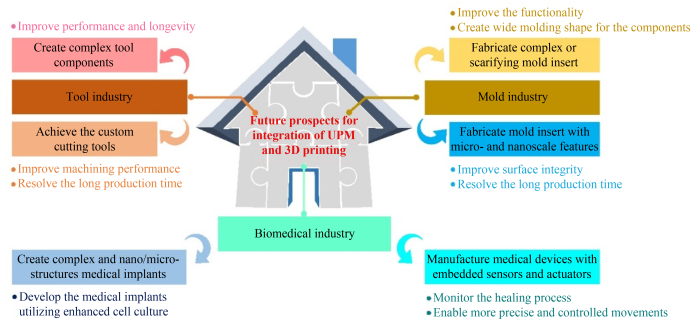
圖3 3D打印和UPM結合的未來前景
原文信息
3D printing for ultra-precision machining: current status, opportunities, and future perspectives
Tao HE, Wai Sze YIP, Edward Hengzhou YAN, Jiuxing TANG, Muhammad REHAN, Long TENG, Chi Ho WONG, Linhe SUN, Baolong ZHANG, Feng GUO, Shaohe ZHANG, Suet TO
Abstract:
Additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing, has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by allowing the production of complex and intricate parts at a lower cost and with greater efficiency. However, 3D-printed parts frequently require post-processing or integration with other machining technologies to achieve the desired surface finish, accuracy, and mechanical properties. Ultra-precision machining (UPM) is a potential machining technology that addresses these challenges by enabling high surface quality, accuracy, and repeatability in 3D-printed components. This study provides an overview of the current state of UPM for 3D printing, including the current UPM and 3D printing stages, and the application of UPM to 3D printing. Following the presentation of current stage perspectives, this study presents a detailed discussion of the benefits of combining UPM with 3D printing and the opportunities for leveraging UPM on 3D printing or supporting each other. In particular, future opportunities focus on cutting tools manufactured via 3D printing for UPM, UPM of 3D-printed components for real-world applications, and post-machining of 3D-printed components. Finally, future prospects for integrating the two advanced manufacturing technologies into potential industries are discussed. This study concludes that UPM is a promising technology for 3D-printed components, exhibiting the potential to improve the functionality and performance of 3D-printed products in various applications. It also discusses how UPM and 3D printing can complement each other.
Cite this article
Tao HE, Wai Sze YIP, Edward Hengzhou YAN, Jiuxing TANG, Muhammad REHAN, Long TENG, Chi Ho WONG, Linhe SUN, Baolong ZHANG, Feng GUO, Shaohe ZHANG, Suet TO. 3D printing for ultra-precision machining: current status, opportunities, and future perspectives. Front. Mech. Eng., 2024, 19(4): 23
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-024-0792-4
來源: Engineering前沿

 科普中國公眾號
科普中國公眾號
 科普中國微博
科普中國微博

 幫助
幫助
 Engineering前沿
Engineering前沿 
